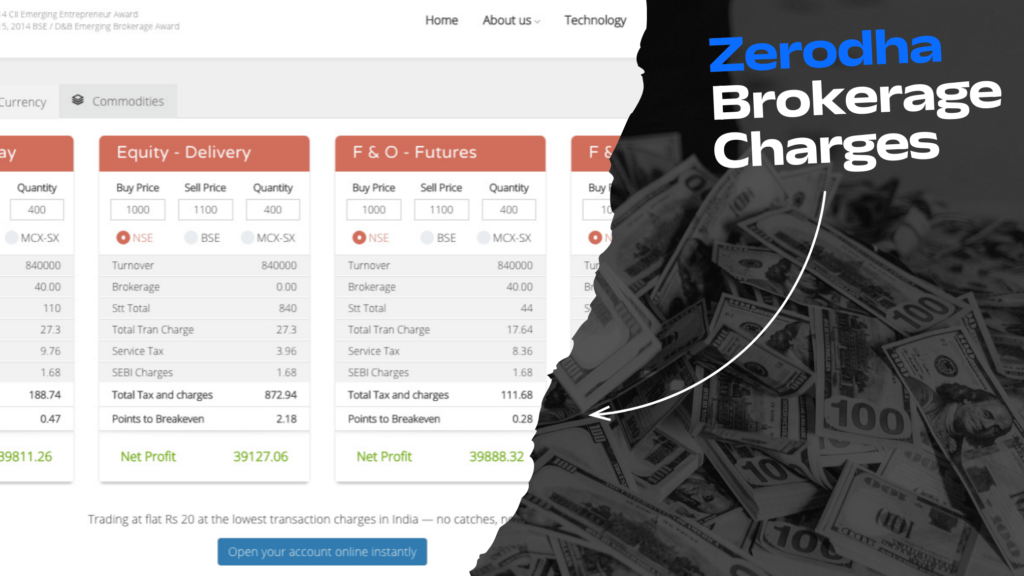
Trading in the stock market involves not only strategic decision-making but also understanding the associated costs. Zerodha, India’s leading discount broker, has revolutionized the brokerage industry with its transparent pricing structure. While it offers competitive brokerage fees, traders need to be aware of all the charges involved to optimize their costs and maximize profits. In this guide, we will explore Zerodha brokerage charges, how they impact trading costs, and ways to save money on trades.
1. Overview of Zerodha Brokerage Charges
Zerodha follows a discount brokerage model, meaning it charges a flat fee instead of a percentage-based commission. This approach benefits active traders and investors who execute multiple trades.
The primary charges include:
- Equity Delivery: Zero brokerage charges, making it cost-effective for long-term investors.
- Equity Intraday, Futures & Options: Flat Rs. 20 or 0.03% per executed order, whichever is lower.
- Currency & Commodity Trading: Flat Rs. 20 per executed order.
- Direct Mutual Funds: No commission or brokerage charges.
Understanding these charges helps traders plan their trades better and avoid unnecessary costs.
2. Breakdown of Additional Trading Charges
Apart from brokerage fees, traders should also consider other charges levied on trades. These include:
a) Exchange Transaction Charges
- Levied by stock exchanges (NSE, BSE, MCX) based on trade volume.
- Varies depending on the trading segment (equities, F&O, commodities, currencies).
b) Securities Transaction Tax (STT)
- Charged by the government on the total transaction value.
- STT for equity delivery trades applies on both buy and sell transactions, whereas, for intraday and derivatives, it applies only to sell transactions.
c) Goods and Services Tax (GST)
- Applied at 18% on brokerage and exchange transaction charges.
- Adds to the overall cost of trading.
d) SEBI Turnover Charges
- A nominal charge levied by SEBI to regulate the securities market.
e) Stamp Duty
- State-imposed charges vary across different Indian states.
By considering all these charges, traders can accurately estimate their total costs.
3. How Brokerage Charges Affect Profitability
Every cost associated with a trade directly impacts the net profit. High-frequency traders, in particular, need to account for these expenses. Understanding brokerage charges allows traders to set appropriate entry and exit points to cover costs and ensure profitability.
For instance, in intraday trading, the frequent buying and selling of shares result in higher cumulative costs, so traders must incorporate brokerage and other charges when setting their profit targets.
4. Ways to Save Money on Brokerage Charges
Reducing brokerage costs can significantly improve trading profitability. Here are some strategies to minimize trading expenses:
a) Opt for Equity Delivery Trading
Since Zerodha does not charge brokerage on equity delivery trades, investors can benefit by holding stocks for the long term.
b) Reduce the Number of Small Trades
Instead of placing multiple small trades, executing fewer but larger trades can help lower transaction costs.
c) Use Limit Orders Instead of Market Orders
Placing limit orders instead of market orders helps traders avoid slippage, thereby optimizing trade execution and reducing potential losses.
d) Take Advantage of Good Till Triggered (GTT) Orders
GTT orders allow traders to set buy or sell triggers in advance, reducing the need for constant monitoring and unnecessary intraday trades.
e) Monitor Total Transaction Costs
Using Zerodha’s brokerage calculator before placing trades provides clarity on costs and helps traders make more informed decisions.
5. Example Calculations for Brokerage Charges
Let’s consider an example to understand the total cost of an intraday trade:
- Buy Price: Rs. 500
- Sell Price: Rs. 510
- Quantity: 100 shares
Upon calculation, the total brokerage, STT, GST, SEBI charges, and transaction fees will determine the net profit. By analyzing these costs, traders can adjust their trade size and target profits accordingly.
6. Hidden Costs to Watch Out For
While Zerodha is transparent with its charges, traders should also be mindful of indirect costs:
- Slippage: The difference between expected and actual execution price.
- Interest on Margin Trades: Holding leveraged positions overnight incurs interest charges.
- DP Charges: Rs. 13.5 per scrip per day for selling shares from a demat account.
Being aware of these costs can help traders make more strategic decisions.
7. Who Benefits the Most from Zerodha Pricing Model?
- Long-Term Investors: Benefit from zero brokerage on equity delivery.
- Options Traders: Flat Rs. 20 per order makes options trading cost-effective.
- Active Intraday Traders: Fixed brokerage helps in managing expenses.
- Beginner Traders: The low-cost structure allows new traders to start without high fees.
8. Zerodha Additional Trading Features to Reduce Costs
Zerodha offers several tools to help traders optimize their costs:
- Brokerage Calculator: Provides an estimate of trading costs before executing a trade.
- Margin Calculator: Helps traders understand leverage and margin requirements.
- Varsity by Zerodha: Free educational resources for improving trading strategies.
Final Thoughts
Understanding Zerodha’s brokerage charges is crucial for any trader looking to save money on trades. By leveraging the zero brokerage model for equity delivery, minimizing unnecessary trades, and using available tools. Traders can significantly reduce their costs and enhance their profitability. Being aware of all charges, including transaction fees, STT, GST, and stamp duty, ensures transparency and helps traders make more informed decisions.