The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a comprehensive indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services in India. Introduced on July 1, 2017, GST replaced multiple indirect taxes such as VAT, excise duty, and service tax, streamlining the taxation system. To accommodate different goods and services, the government has categorized them into different tax slabs. Understanding these GST slabs is essential for businesses and consumers alike. This guide provides an in-depth overview of GST slabs, their rates, and their implications.
Understanding GST Slabs
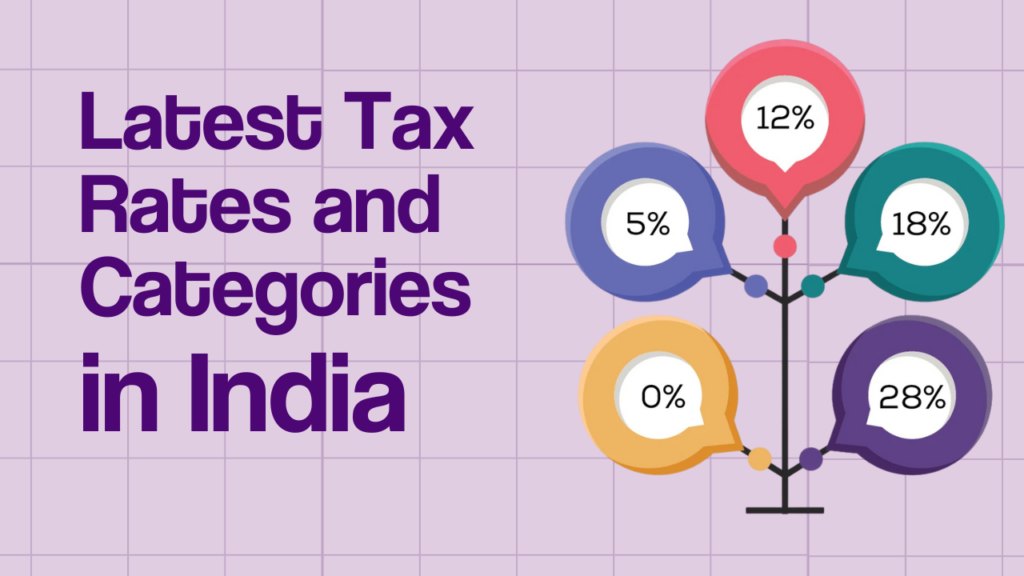
The GST system in India follows a multi-tier tax structure, ensuring that essential goods are taxed at lower rates while luxury and sin goods attract higher taxes. The primary GST slabs are 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%. Each slab applies to different categories of goods and services.
GST Slabs and Their Applicability
1. 0% GST (Exempted Category)
This category includes essential goods and services to ensure affordability and accessibility to the general public. Products under this slab include:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Milk, curd, and eggs
- Unprocessed cereals and grains
- Healthcare and educational services
- Books and newspapers
The 0% tax slab ensures that necessities remain affordable and do not burden consumers.
2. 5% GST (Lower Tax Bracket)
The 5% GST slab covers essential goods and services that are slightly processed but still necessary for daily life. Items in this category include:
- Packaged food items like branded flour and sugar
- Edible oils
- Footwear and clothing under ₹1,000
- Railway tickets (except first class and AC coaches)
- Economy-class air travel
This lower tax rate ensures that essential commodities remain within reach while contributing to tax revenue.
3. 12% GST (Standard Rate – Lower Tier)
The 12% slab applies to goods and services that are not essential but still widely used. Products in this category include:
- Processed foods such as butter and cheese
- Mobile phones
- Fruit juices
- Business-class air travel
- Hotel rooms priced between ₹1,000 and ₹7,500 per night
These items are taxed moderately, balancing affordability and revenue generation.
4. 18% GST (Standard Rate – Higher Tier)
The 18% slab is one of the most widely applicable GST rates, covering various goods and services. Items in this category include:
- Instant food products such as pasta and noodles
- Computers and electronic gadgets
- Branded garments
- Financial services
- AC and non-AC restaurants
- Hotel rooms above ₹7,500 per night
This slab represents a significant portion of taxable transactions in India.
5. 28% GST (Luxury and Sin Goods)
The highest GST slab applies to luxury goods, demerit goods, and items deemed harmful to health or the environment. Products under this category include:
- High-end cars and motorcycles
- Cigarettes and tobacco products
- Aerated beverages and soft drinks
- Luxury hotels and resorts
- Air conditioners and refrigerators
In addition to GST, some items in this category attract Compensation Cess to offset revenue losses for state governments.
Additional GST Categories
Apart from the primary slabs, there are some special tax rates and exemptions:
1. Composition Scheme (1% to 6%)
Small businesses with an annual turnover of up to ₹1.5 crore can opt for the Composition Scheme, which simplifies tax compliance. The applicable rates are:
- 1% for manufacturers and traders
- 5% for restaurants (not serving alcohol)
- 6% for service providers (with turnover up to ₹50 lakh)
Under this scheme, businesses pay a fixed GST rate and cannot claim Input Tax Credit (ITC).
2. Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM)
Certain transactions require the recipient, instead of the supplier, to pay GST. This applies to:
- Purchases from unregistered suppliers
- Import of services
- Certain notified services such as legal services
RCM ensures tax compliance and prevents evasion.
How GST Slabs Impact Businesses and Consumers
GST rates influence both pricing and demand for goods and services. Here’s how different stakeholders are affected:
1. Impact on Consumers
- Lower tax rates on essential goods keep daily necessities affordable.
- Higher GST on luxury goods increases their cost, discouraging unnecessary expenditure.
- Transparency in taxation prevents hidden charges.
2. Impact on Businesses
- Uniform tax rates simplify compliance and reduce tax evasion.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC) allows businesses to claim credit on taxes paid for inputs, reducing costs.
- Classification of goods and services under the right slab is crucial to avoid penalties.
3. Impact on the Economy
- A structured tax regime boosts economic growth by reducing cascading taxes.
- GST slabs encourage fair competition by removing tax barriers between states.
- Revenue generated helps in infrastructural and social development.
Challenges in GST Slabs
Despite its benefits, GST slab classification poses challenges such as:
- Frequent rate changes create confusion among businesses.
- Disputes over classification (e.g., whether a product falls under 12% or 18%).
- High tax on certain goods, leading to black-market activities.
Final Thoughts
Understanding GST slabs is essential for businesses, consumers, and policymakers. The multi-tier system ensures affordability for essential goods while maintaining revenue collection through higher taxes on luxury items. Staying updated with GST rates and compliance requirements helps businesses optimize pricing and taxation strategies. As India’s taxation system evolves, GST rates may change, making it crucial to stay informed about the latest updates.