NASA has successfully retrieved a capsule carrying rare asteroid samples collected from a near-Earth asteroid. Marking a significant achievement in space exploration. This mission is part of NASA broader effort to understand the origins of the solar system and the building blocks of life.
Sample Return After Years in Space
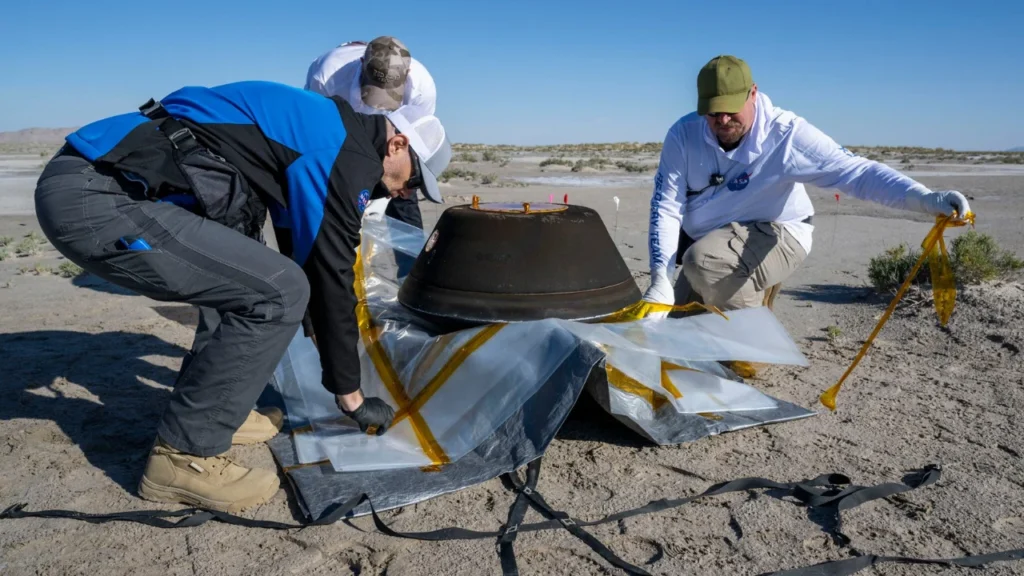
The capsule, released by the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft, landed in the Utah desert after traveling for more than seven years in space. It contained material collected from the asteroid Bennu, which scientists believe has remained largely unchanged for billions of years. A team of researchers and engineers quickly recovered the capsule after it parachuted safely to the ground.
Scientists have estimated that the capsule may hold around 250 grams of rocky material. Making it the largest quantity of asteroid sample ever returned to Earth by a U.S. mission. In 2020, OSIRIS-REx briefly touched the surface of Bennu and used its robotic arm to collect surface debris.
Unlocking Clues to Planetary Origins
Scientists expect the asteroid samples to provide valuable insights into the early solar system. Including how planets formed and how water and organic compounds may have been delivered to Earth. Researchers will spend months carefully analyzing the material in specialized labs to avoid contamination and preserve its original state.
Early assessments indicate the presence of carbon-rich compounds. Which could support theories that asteroids like Bennu contributed to the formation of life on Earth. The mission team will distribute portions of the sample to research institutions around the world for further study.
OSIRIS-REx to Continue Its Journey
Following the release of the capsule, OSIRIS-REx has been renamed OSIRIS-APEX and is now on a new course. To study another asteroid named Apophis, which it is expected to reach in 2029. This extended mission aims to gather more data about the behavior and structure of asteroids that could pose a threat to Earth.
NASA successful completion of this sample return mission sets a strong precedent for future deep-space exploration and research. Giving scientists a rare opportunity to directly study material from the early solar system.