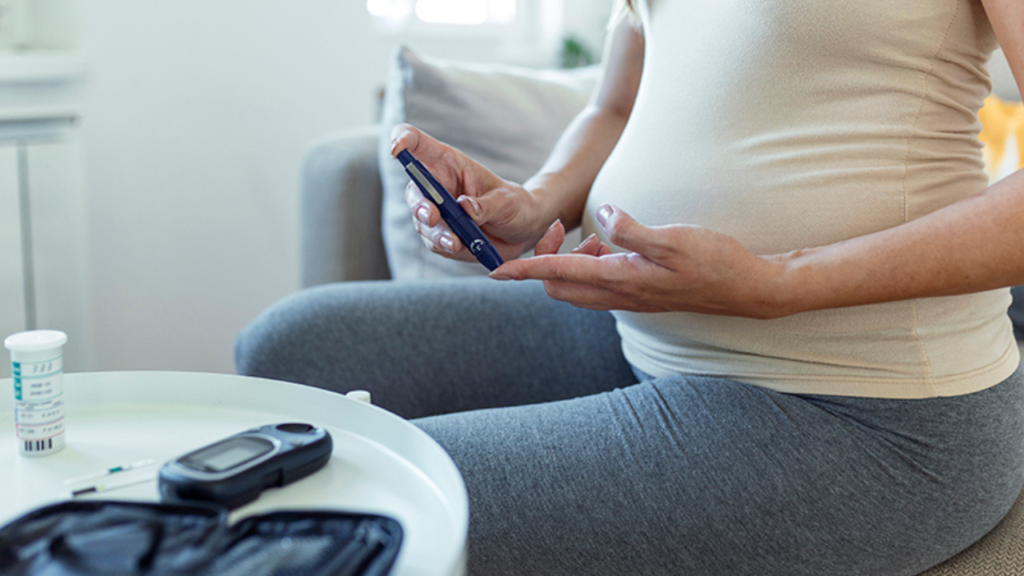
Diabetes during pregnancy—whether pre-existing (type 1 or 2) or gestational—poses serious risks for both mother and child. Poor blood sugar control significantly increases chances of premature delivery, stillbirth, and neonatal complications.
Dangers of Uncontrolled Diabetes in Pregnancy
High maternal glucose can lead to stillbirth after 20 weeks, as elevated blood sugar damages the placenta and impairs fetal oxygen supply—studies show up to a fourfold increase in stillbirth risk. Babies born to mothers with type 2 diabetes face a 5× higher stillbirth rate. Additionally, diabetes can trigger preterm birth (before 37 weeks), often requiring early labour induction or C-section to avoid further issues.
Neonatal Health Concerns
When mothers have elevated blood sugar, glucose crosses the placenta into the fetus, stimulating excess insulin and causing:
- Macrosomia: Babies larger than normal, increasing risk of C-section and birth injuries.
- Neonatal hypoglycaemia: Low blood sugar soon after birth; infants born to mothers with gestational diabetes are 10× more likely to experience this, and risk is even higher with pre-pregnancy diabetes.
- Respiratory distress and jaundice are also more common.
Importance of Tight Glucose Controls
Proper management—via diet, exercise, regular insulin or medication—significantly lowers risks. Tight glucose control has been shown to reduce stillbirth by around 10%. Mothers should undergo early prenatal screening (24–28 weeks for gestational diabetes, earlier if pre-existing). Monitoring includes fasting tests, glucose tolerance tests, and routine fetal checks.
Lasting Risks for Mother and Child
Women with gestational diabetes face a 30–50% chance of developing type 2 diabetes within a decade. Children born to diabetic mothers run higher long-term risks of obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome.