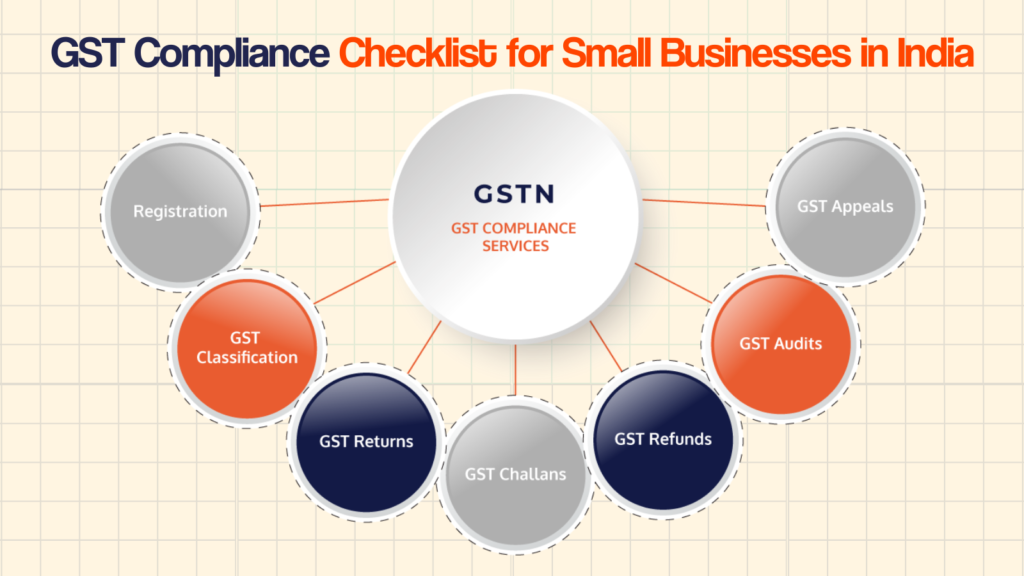
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a crucial tax reform in India that ensures transparency and streamlines the taxation process. For small businesses, staying GST-compliant is essential to avoid penalties and ensure smooth operations. Non-compliance can lead to heavy fines, business disruptions, and loss of input tax credit benefits. This guide provides a comprehensive GST compliance checklist, covering registration, invoicing, returns, payments, and record-keeping to help small businesses navigate GST regulations effectively.
GST Registration Compliance
GST registration is mandatory for businesses that exceed the prescribed turnover threshold. Small businesses should ensure the following:
- Register for GST if turnover exceeds Rs. 40 lakh (Rs. 10 lakh for special category states).
- Obtain a valid GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) upon successful registration.
- Display GSTIN prominently on business premises and on invoices to maintain transparency.
- Renew GST registration if applicable and keep business details updated on the GST portal.
- Composition scheme eligibility: Businesses with turnover up to Rs. 1.5 crore can opt for the Composition Scheme to pay tax at a fixed rate.
Proper Invoicing and Documentation
- Issue GST-compliant invoices that include:
- Unique invoice number and date
- Supplier and recipient details (name, address, and GSTIN)
- HSN/SAC codes for goods/services as per GST classification
- Taxable value and applicable tax rates (CGST, SGST, IGST)
- Terms of supply and payment details
- Maintain copies of invoices (both digital and physical) for at least six years as per GST regulations.
- Use an automated invoicing system to reduce errors and ensure compliance with GST norms.
- Generate credit and debit notes for sales returns or amendments in invoices.
Filing GST Returns on Time
GST return filing is a critical compliance requirement. Businesses must identify and file the correct returns as per their category:
- GSTR-1: Monthly/quarterly return for reporting outward supplies.
- GSTR-3B: Monthly summary return for tax liability and Input Tax Credit (ITC) claims.
- GSTR-4: Quarterly return for Composition Scheme taxpayers.
- GSTR-9: Annual return for regular taxpayers to consolidate yearly transactions.
- Ensure timely filing to avoid penalties and interest charges.
- Reconcile sales, purchases, and ITC with GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B reports before filing.
- Maintain proper documentation to substantiate return filings in case of audits or assessments.
Payment of GST Dues
- Accurately calculate GST liability based on taxable transactions.
- Pay GST dues before the deadline to avoid late fees and interest charges.
- Use the correct tax payment codes (CGST, SGST, IGST) while making payments through the GST portal.
- Maintain records of tax payments, challans, and payment receipts for future reference.
Input Tax Credit (ITC) Compliance
Proper management of Input Tax Credit (ITC) helps businesses reduce their tax liability. Small businesses must ensure:
- Claim ITC only on eligible purchases used for business purposes.
- Ensure suppliers file their returns on time to reflect ITC in GSTR-2B.
- Maintain proper documentation of purchase invoices and receipts to support ITC claims.
- Reverse ITC if payments to suppliers are not made within 180 days as per GST rules.
- Avoid claiming ITC on exempted or non-business-related expenses to prevent penalties.
GST E-Way Bill Compliance
The e-Way Bill system is crucial for transporting goods across state borders. Businesses must ensure:
- Generate e-Way Bills for inter-state transportation of goods exceeding Rs. 50,000.
- Carry a valid e-Way Bill during transportation to avoid penalties and goods seizure.
- Maintain records of all e-Way Bills generated and used for audit purposes.
- Use an e-Way Bill tracking system to ensure compliance and avoid disruptions in logistics.
GST Audit and Record-Keeping
Regular audits and proper record-keeping are essential for GST compliance. Businesses should:
- Maintain records of sales and purchase invoices, tax payment receipts, GST returns filed, and e-Way Bills.
- Retain GST-related documents for a minimum of six years to comply with tax regulations.
- Prepare for periodic GST audits and assessments by tax authorities.
- Conduct self-audits to identify discrepancies and rectify errors before tax department audits.
Compliance for E-Commerce Sellers
E-commerce businesses are subject to additional GST compliance requirements. Small businesses selling online must:
- Register for GST if selling via e-commerce platforms like Flipkart, Amazon, or Myntra.
- File GSTR-8 if they are Tax Collected at Source (TCS) operators.
- Reconcile sales with platform-generated reports to avoid mismatches and discrepancies.
- Ensure compliance with GST rules related to marketplace sellers and TCS deductions.
Composition Scheme Compliance
Small businesses opting for the Composition Scheme must:
- Ensure annual turnover does not exceed Rs. 1.5 crore to remain eligible.
- Pay GST at a fixed percentage of turnover instead of standard tax rates.
- File GSTR-4 quarterly and GSTR-9A annually to report tax payments.
- Note that businesses under the Composition Scheme cannot claim ITC.
- Maintain proper records of transactions as per scheme guidelines to avoid penalties.
Handling GST Notices and Assessments
Small businesses should be prepared for notices and assessments from the GST department. Key actions include:
- Regularly checking the GST portal and email for any notices from tax authorities.
- Responding promptly to GST inquiries and assessments to avoid escalations.
- Rectifying errors in GST return filings to prevent penalties and disputes.
- Seeking professional assistance for complex notices or legal matters related to GST.
Avoiding Common GST Compliance Mistakes
To maintain seamless GST compliance, small businesses must avoid the following mistakes:
- Incorrect GST registration details: Ensure business details match PAN records and avoid errors in GSTIN.
- Mismatched invoice details: Ensure invoices match reported sales figures to prevent discrepancies.
- Late GST return filings: Missing deadlines results in penalties and loss of input tax credit.
- Improper ITC claims: Claiming ineligible ITC can lead to penalties and interest charges.
- Neglecting e-Way Bill requirements: Failing to generate e-Way Bills can lead to fines and transportation delays.
Final Thought
GST compliance is crucial for small businesses in India to operate legally and efficiently. By following this comprehensive checklist, businesses can ensure proper registration, accurate invoicing, timely tax payments, and effective record-keeping. Staying updated with GST regulations and seeking professional help when necessary can help businesses avoid penalties and maintain smooth operations. A proactive approach to GST compliance ensures financial stability and strengthens business credibility in the long run.