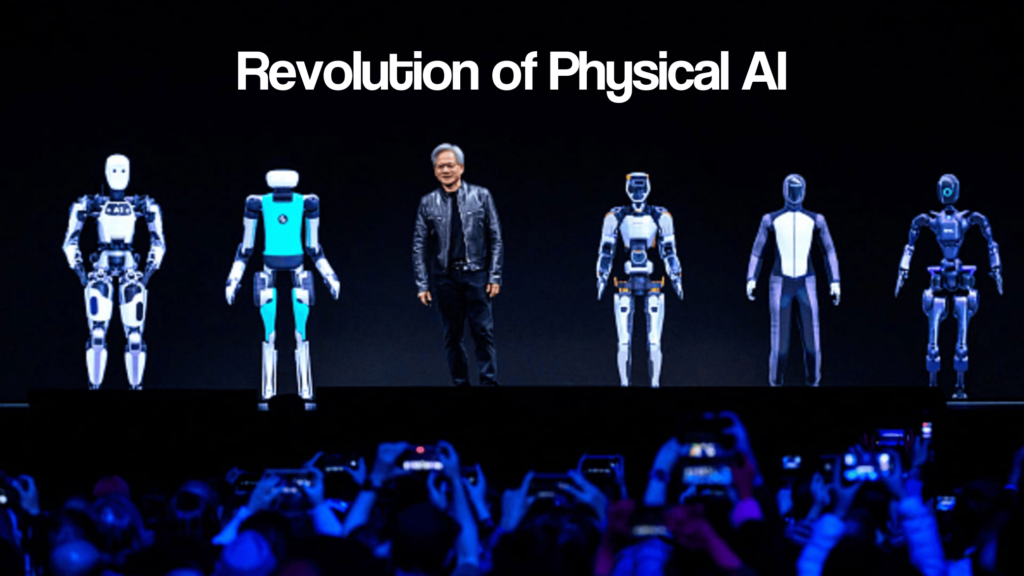
Physical AI refers to the integration of artificial intelligence with robotic and physical systems, enabling machines to perceive, learn, and interact intelligently with their environment. The concept has its roots in the early advancements of robotics and AI in the mid-20th century when researchers sought to create machines that could not only process data but also perform complex physical tasks. With the rise of deep-learning, computer vision, and advanced sensors, Physical AI has evolved into a field that bridges the gap between cognitive AI and real-world embodiment, allowing robots and autonomous systems to navigate and operate in dynamic environments.
This fusion of AI and robotics has had a transformative influence across industries. In healthcare, AI-driven prosthetics and robotic-assisted surgeries are enhancing patient care. Autonomous vehicles and drones are revolutionizing transportation and Supply chain. Smart manufacturing systems powered by Physical AI are optimizing industrial automation, while humanoid robots are being developed for applications ranging from customer service to space exploration. As advancements continue, the future of Physical AI holds the promise of more intelligent, adaptable, and human-like machines, fundamentally reshaping how technology interacts with the physical world.
Applications of Physical AI in Everyday Life: Where AI Meets the Real World
- Healthcare & Biomedicine – Physical AI is transforming healthcare with robotic-assisted surgeries, AI-powered prosthetics, and smart rehabilitation devices. Surgical robots enhance precision, while AI-driven diagnostics improve patient outcomes.
- Autonomous Vehicles – Self-driving cars and AI-controlled drones use advanced sensors, computer vision, and deep-learning to navigate roads and airspace safely, reducing human errors and optimizing transportation efficiency.
- Industrial Automation – Smart factories harness AI-powered robotic arms and automated systems for efficient manufacturing, assembly, and quality control, leading to increased productivity and reduced operational costs.
- Space Exploration – AI-driven rovers, autonomous spacecraft, and humanoid robots assist in planetary exploration, maintenance, and space research, enabling missions to extreme environments beyond human capabilities.
- Assistive Robotics – AI-driven exoskeletons aid individuals with mobility impairments, while robotic caregivers assist the elderly and disabled, improving independence and quality of life.
- Agriculture & Precision Farming – AI-powered robots and drones optimize farming operations by monitoring crops, automating harvesting, and improving resource management through data-driven insights.
- Defense & Security – AI-enhanced robotic systems assist in surveillance, bomb disposal, and reconnaissance missions, improving national security while minimizing risks to human personnel.
AI in the Physical World: Overcoming the Limitations and Pitfalls
Despite its immense potential, Physical AI faces several hurdles, including hardware constraints, ethical concerns, data limitations, regulatory challenges, high costs, and trust issues. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the safe and effective integration of AI into real-world applications.
- Hardware Limitations – AI systems require high computational power, long-lasting battery life, and durable materials to function efficiently, but current technology still struggles to meet these demands.
- Ethical Concerns – AI-driven physical systems raise concerns about decision-making transparency, job displacement due to automation, and potential safety risks in unpredictable environments.
- Data & Learning Constraints – Training AI for real-world interactions is challenging due to limited high-quality data, environmental unpredictability, and the difficulty of simulating all possible scenarios.
- Regulatory & Safety Issues – The lack of standardized global regulations for AI in physical applications leads to inconsistencies in safety protocols, legal accountability, and ethical considerations.
- Cost & Accessibility – Developing and deploying Physical AI requires significant investment, limiting its accessibility for smaller industries and emerging markets.
- Human-AI Interaction & Trust – Ensuring that AI-driven physical systems are safe, reliable, and widely accepted by humans remains a challenge, as trust in autonomous technology is still developing.
Conclusion
Physical AI represents a groundbreaking fusion of artificial intelligence and robotics, enabling machines to interact intelligently with the real world. From healthcare and autonomous vehicles to space exploration and assistive robotics, its applications are rapidly expanding, transforming industries and enhancing human capabilities. As advancements in machine learning, computer vision, and sensor technologies continue, This AI systems is poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of automation and intelligent systems.
However, significant challenges remain, including hardware limitations, ethical concerns, data constraints, and regulatory hurdles. Addressing these issues will require collaborative efforts from researchers, policymakers, and industry leaders to ensure that Physical AI is developed responsibly and safely. With continued revolution and proper safeguards, this AI has the potential to revolutionize the way humans and intelligent machines coexist and interact in the real world.